Accommodation of Regional Aspirations in India
- Linguistic Reorganization
- Regional Aspirations: Case Study of North-East India
- Autonomy and Secessionism: Punjab & Nagaland
- Statehood and Sub-Regional Movements: Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh & Uttarakhand
(Easy language, suitable for 10–20 marks)
Introduction
India is a diverse country with multiple languages, cultures, regions, and ethnic identities.
To maintain unity, the Indian state has accommodated regional aspirations through constitutional, political, and administrative measures such as linguistic reorganization, autonomy, statehood, and federal decentralisation.
1. Linguistic Reorganization of States

Meaning
Linguistic reorganization means restructuring states on the basis of language spoken by the majority of people.
Background
- Demand began after independence
- Potti Sriramulu’s movement (1952) led to the formation of Andhra Pradesh (1953)
- States Reorganisation Act, 1956 reorganised states mainly on linguistic lines
Objectives
- Administrative convenience
- Protection of linguistic identity
- National integration
Impact
Positive
- Reduced linguistic conflicts
- Strengthened democracy & federalism
- Improved administration
Negative
- Fear of regionalism
- Inter-state disputes
👉 Overall, linguistic reorganization is considered a successful accommodation of regional aspirations.
2. Regional Aspirations: Case Study of North-East India
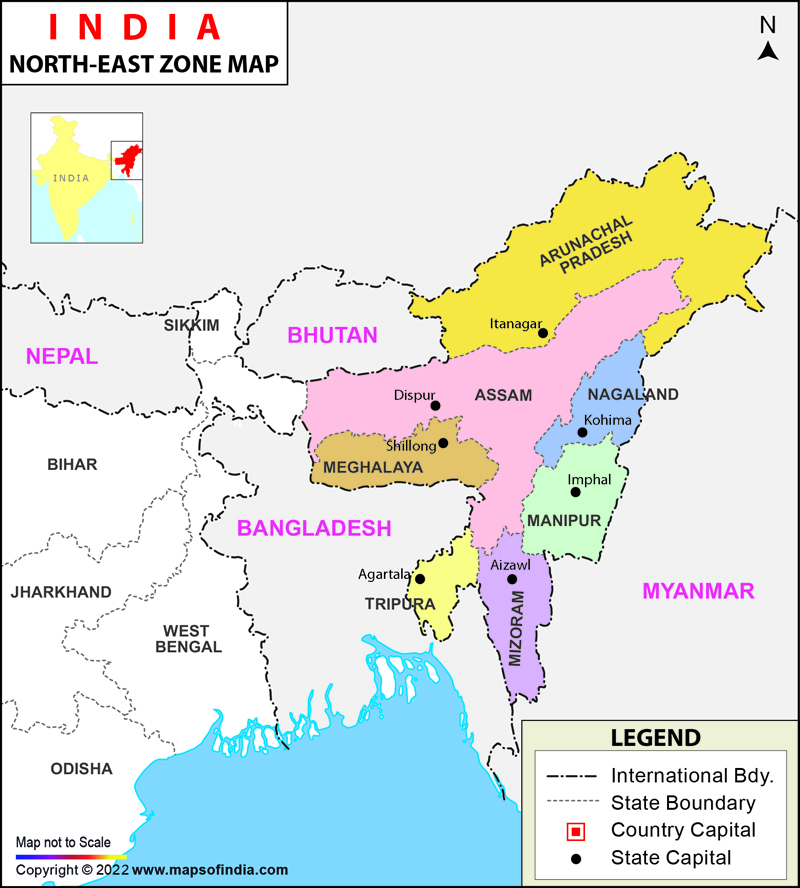


Background
North-East India is ethnically, linguistically, and culturally distinct.
The region faced:
- Historical isolation
- Economic underdevelopment
- Ethnic diversity
- Border issues
Major Aspirations
- Protection of tribal identity
- Political autonomy
- Economic development
- Security and dignity
Government Responses
- Creation of new states (Nagaland, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh)
- Sixth Schedule (Autonomous District Councils)
- Special provisions (Article 371)
- Peace accords (Mizo Accord, Bodo Accord)
Outcome
- Reduced insurgency in many areas
- Political inclusion of ethnic groups
- Ongoing challenges in some regions
3. Autonomy and Secessionism: Punjab & Nagaland
A. Punjab


Nature of the Movement
- Demand for greater autonomy
- Anandpur Sahib Resolution
- Later escalated into secessionist Khalistan movement
Government Response
- Political negotiations
- Punjab Accord (1985)
- Restoration of democratic process
Result
- Secessionism declined
- State returned to normal democratic functioning
B. Nagaland



Nature of the Movement
- Ethnic identity-based movement
- Demand for sovereignty
Government Response
- Creation of Nagaland state (1963)
- Special status under Article 371A
- Ongoing peace talks
Result
- Partial accommodation
- Peace process still continuing
4. Statehood & Sub-Regional Movements



Meaning
Sub-regional movements arise within states due to:
- Cultural identity
- Economic neglect
- Administrative distance
A. Jharkhand (2000)
- Tribal identity movement
- Demand for development & resource control
- Carved out of Bihar
B. Chhattisgarh (2000)
- Administrative efficiency
- Tribal welfare
- Separated from Madhya Pradesh
C. Uttarakhand (2000)
- Hill region neglect
- Demand for development & self-governance
- Separated from Uttar Pradesh
Significance
- Improved governance
- Greater political participation
- Recognition of regional identity
Conclusion
India has adopted a flexible and democratic approach to accommodate regional aspirations through:
- Linguistic reorganization
- Autonomy provisions
- Creation of new states
- Peace accords
These measures have strengthened Indian federalism, reduced conflicts, and preserved national unity while respecting diversity.
📌 UG Exam Tips
✔ Write examples with years
✔ Use headings & case studies
✔ Mention positives & limitations
✔ End with a balanced conclusion
If you want:
✔️ Short notes (2–5 marks)
✔️ MCQs with answer key
✔️ PDF notes
✔️ Hindi / Odia version
Just tell me 😊






