- Political Defection in India
- Coalition Politics and Parties
- Role of Opposition Parties in the Indian Parliamentary System
(Language is easy, points are clear, suitable for 10–20 mark answers)
1. Political Defection in India


Meaning of Political Defection
Political defection refers to the situation when an elected representative (MP or MLA) changes his/her political party after elections or votes against the party line.
In simple words:
👉 “Party badalna after election”
Reasons for Political Defection
- Desire for power or ministerial position
- Personal ambition
- Party conflicts and leadership disputes
- Money, influence, or pressure
- Weak party discipline
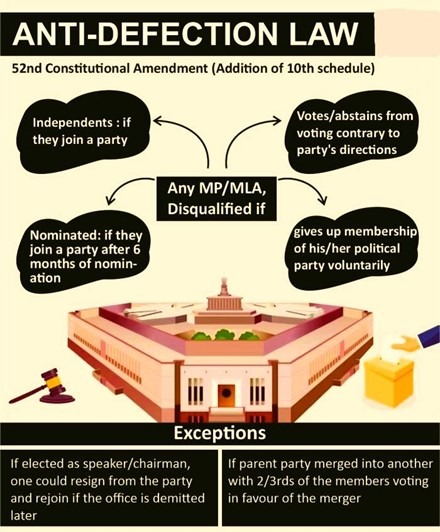
Anti-Defection Law (1985)
To control defections, the 52nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1985 added the 10th Schedule to the Constitution.
Main Provisions
- A member is disqualified if:
- He/she voluntarily gives up party membership
- Votes against party whip
- Independent members cannot join any party after election
- Nominated members must join a party within 6 months
Decision Authority
- Speaker/Chairman of the House decides disqualification
Importance of Anti-Defection Law
✅ Prevents political instability
✅ Strengthens party discipline
✅ Ensures respect for voters’ mandate
Criticism
❌ Limits freedom of speech of legislators
❌ Speaker’s decision may be biased
❌ Encourages “mass defections”
2. Coalition Politics and Parties



Meaning of Coalition Politics
Coalition politics means multiple political parties come together to form a government when no single party gets a clear majority.
Growth of Coalition Politics in India
- Started prominently after 1989
- Decline of single-party dominance
- Rise of regional parties
- Diverse social and regional interests
Major Coalition Governments
- National Front (1989)
- NDA (1998–2004, 2014– )
- UPA (2004–2014)
Role of Political Parties in Coalitions
- National parties provide leadership
- Regional parties act as kingmakers
- Parties negotiate policies and portfolios
- Shared minimum programme (CMP)
Merits of Coalition Politics
✅ Represents diversity
✅ Strengthens federalism
✅ Prevents authoritarianism
✅ Encourages consensus politics
Demerits
❌ Instability of government
❌ Policy delays
❌ Small parties exercise disproportionate power
3. Role of Opposition Parties in Indian Parliamentary System



Meaning of Opposition
Opposition consists of all political parties not in power in Parliament or State Legislatures.
Functions of Opposition Parties
1. Watchdog of Democracy
- Keeps check on government actions
- Prevents misuse of power
2. Criticism & Accountability
- Questions policies, laws, and spending
- Uses Question Hour, Zero Hour, debates
3. Representation of Public Opinion
- Raises issues of common people
- Voices grievances ignored by government
4. Alternative Government
- Provides alternative policies and leadership
- Ready to replace government if voted to power
5. Role in Law-Making
- Suggests amendments
- Participates in parliamentary committees
Leader of Opposition
- Head of the largest opposition party
- Plays key role in:
- Appointments (CVC, Lokpal, etc.)
- Parliamentary discussions
Importance of Strong Opposition
✅ Essential for healthy democracy
✅ Improves quality of governance
✅ Protects constitutional values
Conclusion
Political defection, coalition politics, and opposition parties are interconnected aspects of Indian democracy.
While defections and coalition instability create challenges, a strong opposition and effective laws help maintain democratic balance, accountability, and federal spirit in India.
📌 For Exam Use
- This answer is suitable for UG Multidisciplinary Courses
- Can be written as:
- 3 short notes
- One long answer
- Separate 10-mark answers
If you want:
✔️ Short notes version
✔️ MCQs with answers
✔️ PDF for download
✔️ Odia / Hindi version
Just tell me 👍






