Affirmative Action Policies in India: Sources, Directions and Implications
With Special Reference to Adivasis, Reservation Policy and Women
Introduction
Indian society has been marked by deep social and economic inequalities based on caste, class, gender, and tribal identity. To correct these historical injustices, the Indian Constitution provides for Affirmative Action policies—special measures designed to promote equality, social justice, and inclusive development.
This article discusses:
- Sources and directions of affirmative action in India
- Its implications for class, caste, and tribes
- The Forest Rights Act as a case of affirmative action for Adivasis
- Reservation policy in India
- Affirmative action for women
1. Meaning of Affirmative Action
Affirmative Action refers to state-sponsored policies and programs that provide special support and protection to socially and economically disadvantaged groups to ensure substantive equality, not just formal equality.
👉 It aims to level the playing field by compensating for historical discrimination.
2. Sources of Affirmative Action in India



A. Constitutional Sources
- Preamble – Justice (social, economic, political)
- Article 14 – Equality before law
- Article 15(4), 15(5) – Special provisions for SCs, STs, OBCs
- Article 16(4) – Reservation in public employment
- Article 17 – Abolition of untouchability
- Article 46 – Promotion of SC/ST and weaker sections
B. Historical and Social Sources
- Legacy of caste discrimination
- Tribal marginalisation
- Gender inequality
- Economic deprivation
3. Directions of Affirmative Action Policies
Affirmative action in India moves in multiple directions:
1. Political
- Reserved seats for SCs/STs in Parliament and State Assemblies
- Reservation for women in Panchayati Raj institutions
2. Educational
- Reservation in educational institutions
- Scholarships and hostels
- Relaxation in eligibility criteria
3. Economic
- Welfare schemes
- Land rights and livelihood protection
- Skill development programs
4. Legal and Protective
- Anti-discrimination laws
- Protection from exploitation and atrocities
4. Implications for Class, Caste and Tribes
Positive Implications
✅ Increased access to education and employment
✅ Political representation of marginalised groups
✅ Emergence of new middle classes among SCs, STs, and OBCs
✅ Strengthening of democratic inclusion
Challenges
❌ Unequal benefits within beneficiary groups
❌ “Creamy layer” debate
❌ Social resentment and political controversy
❌ Implementation gaps
5. Affirmative Action for Adivasis: The Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006



Background
Adivasis were historically displaced due to:
- Colonial forest laws
- Development projects
- Denial of traditional forest rights
Forest Rights Act, 2006
The FRA aims to:
- Recognize individual and community forest rights
- Protect traditional livelihoods
- Empower Gram Sabhas
Significance as Affirmative Action
- Restores historical injustice
- Ensures land security
- Strengthens tribal self-governance
- Promotes sustainable development
Limitations
- Poor implementation
- Administrative delays
- Conflict with forest bureaucracy
6. Reservation Policy in India
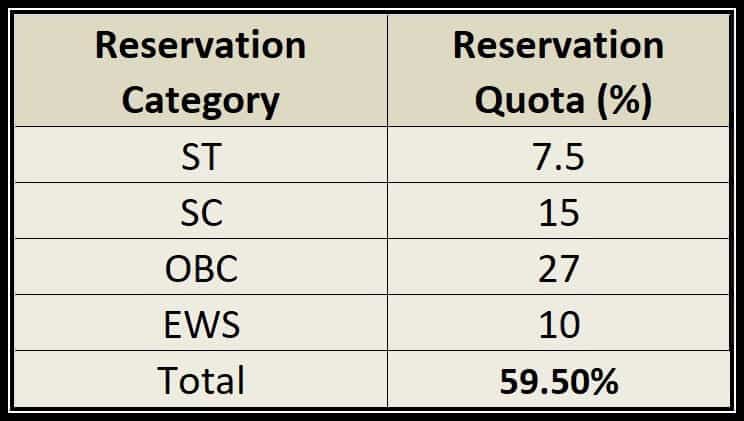


Meaning
Reservation is the allocation of a fixed percentage of seats in education, employment, and politics for disadvantaged groups.
Categories
- SCs and STs – Based on social exclusion
- OBCs – Based on social and educational backwardness
- EWS – Based on economic criteria
Objectives
- Ensure representation
- Reduce inequality
- Promote social justice
Debates
- Merit vs social justice
- Demand for sub-categorisation
- Duration and extent of reservation
7. Affirmative Action for Women



Need
Women face:
- Patriarchy
- Lower workforce participation
- Underrepresentation in politics
Key Measures
- Reservation in Panchayats and Municipalities (33% and above)
- Education incentives for girls
- Maternity benefits and welfare schemes
- Legal safeguards against discrimination
Impact
- Increased political participation of women
- Improved focus on health, education, and welfare
- Gradual empowerment at grassroots level
8. Overall Assessment
Affirmative action in India is not charity, but a constitutional obligation aimed at creating real equality. It has contributed to:
- Social mobility
- Political inclusion
- Democratization of power
However, its success depends on:
- Effective implementation
- Periodic review
- Balancing equity with efficiency
Conclusion
Affirmative Action policies in India reflect the constitutional vision of social justice and inclusive democracy. From reservation policies to tribal rights and women’s empowerment, these measures have transformed Indian society. While challenges remain, affirmative action continues to be a vital instrument for correcting historical injustices and ensuring dignity and opportunity for all citizens.
📌 UG Exam Writing Tips
- Start with definition
- Mention constitutional articles
- Use one case study (FRA)
- Write positives + challenges
- End with a balanced conclusion
If you want:
✔️ Short notes (2–5 marks)
✔️ MCQs / Objective questions
✔️ PDF notes for revision
✔️ Hindi / Odia version
Just tell me 😊






