Introduction
The banking system plays a crucial role in the functioning of a modern economy. It mobilizes savings, provides credit, supports trade and industry, and ensures financial stability. In India, the banking system operates in a hierarchical structure, with commercial banks serving the public and the central bank (Reserve Bank of India) regulating and guiding the entire system.
This module helps students understand how banks function and how central banks influence the financial system through credit control and monetary policy.
1. Commercial Banking: Meaning and Functions


Meaning
A commercial bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and provides loans and other financial services to individuals, businesses, and the government with the objective of earning profit.
Examples: SBI, PNB, Bank of Baroda, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank
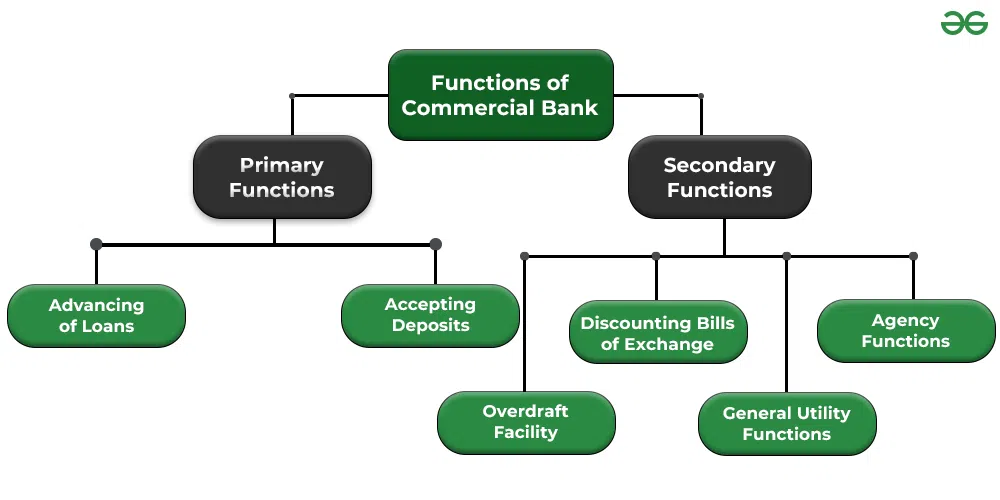
Functions of Commercial Banks
A. Primary Functions
- Accepting Deposits
- Savings deposits
- Current deposits
- Fixed deposits
- Granting Loans and Advances
- Personal and consumer loans
- Business and industrial loans
- Agricultural and housing loans
B. Secondary Functions
- Agency services (collection of cheques, payment of bills)
- Utility services (ATM, debit/credit cards, internet banking)
- Remittance of funds
- Safe custody and locker facilities
2. Process of Credit Creation



Meaning
Credit creation refers to the process by which commercial banks create additional credit through deposits and loans, using only a fraction of their total deposits as reserves.
Process
- A customer deposits money in a bank
- Bank keeps a part as reserve (CRR)
- Remaining amount is given as loan
- Loan amount is redeposited in banks
- Multiple rounds of lending create more credit
Limitations
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- Public’s preference for cash
- RBI regulations
- Demand for loans
3. Concept of Micro-Finance



Meaning
Micro-finance refers to the provision of small loans and basic financial services to low-income groups who lack access to formal banking institutions.
Objectives
- Poverty alleviation
- Women empowerment
- Promotion of self-employment
Institutions
- Self Help Groups (SHGs)
- Micro-Finance Institutions (MFIs)
- NABARD-supported SHG–Bank linkage
4. Central Banking: Meaning and Functions



Meaning
A central bank is the apex monetary authority of a country that regulates the banking system and controls money supply.
In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as the central bank.
Functions of Central Bank (RBI)
- Issue of Currency
- Sole authority to issue currency notes (except ₹1 notes)
- Banker’s Bank
- Provides loans to commercial banks
- Maintains bank reserves
- Banker to the Government
- Manages government accounts
- Issues treasury bills and government bonds
- Controller of Credit
- Regulates credit to maintain economic stability
- Custodian of Foreign Exchange
- Manages foreign exchange reserves
- Maintains exchange rate stability
5. Methods of Credit Control



A. Quantitative Methods
- Bank Rate
- Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR)
- Open Market Operations
B. Qualitative Methods
- Selective credit controls
- Moral suasion
- Credit rationing
- Direct action
6. Recent Reforms in the Banking Sector in India



Major Reforms
- Nationalisation of banks
- Entry of private and foreign banks
- Digital banking and fintech
- Financial inclusion (Jan Dhan Yojana)
- Bank mergers and consolidation
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC)
Objectives
- Improve efficiency
- Reduce NPAs
- Strengthen financial stability
- Promote inclusive growth
7. Monetary Policy: Objectives and Limitations (India)



Meaning
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the Reserve Bank of India to regulate money supply and credit conditions in the economy.
Objectives
- Price stability (inflation control)
- Economic growth
- Full employment
- Financial stability
- Exchange rate stability
Limitations
- Large informal sector
- Weak policy transmission
- Supply-side inflation
- Fiscal dominance
- Banking sector weaknesses
Learning Outcome (LO)
After studying this module, students will:
- Understand the banking hierarchy in India
- Learn how commercial and central banks function
- Know the process of credit creation
- Understand RBI’s role in credit control and monetary policy
- Analyze how central banks influence the financial system and economy
Conclusion
The Indian banking system forms the backbone of economic development. Commercial banks facilitate savings and investment, while the Reserve Bank of India ensures stability through regulation, credit control, and monetary policy. Despite challenges, continuous reforms and digital transformation are strengthening India’s financial system and supporting inclusive growth.
📌 UG Exam Tips
- Write clear definitions
- Use diagrams/examples for credit creation
- Mention RBI tools
- Write objectives + limitations
- End with a short conclusion
If you want:
✔️ Short notes (2–5 marks)
✔️ MCQs with answers
✔️ PDF notes for revision
✔️ Hindi / Odia medium version
Just tell me 😊
Want to keep using GPT-5? Try Go for free.Upgrade your plan to keep getting better, faster answers.
Try Go free




