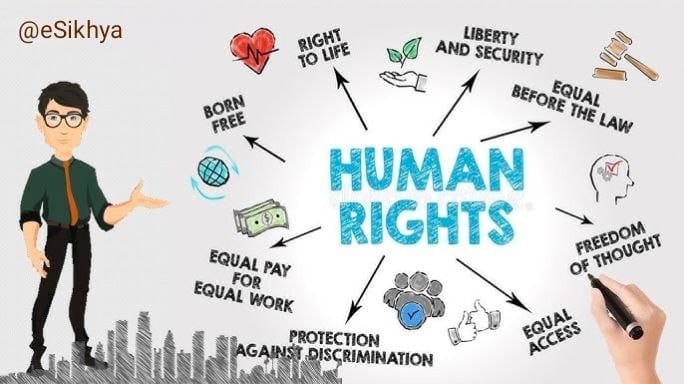
Human rights are the basic rights and freedoms that belong to every person in the world, from birth until death. These rights are based on shared values like dignity, fairness, equality, respect, and independence. They are often set out in law, in international human rights treaties, national constitutions, and other laws.
Human rights are the basic rights and freedoms that belong to every individual simply because they are human. These rights are considered universal and inalienable, meaning they apply to everyone, everywhere, and cannot be taken away.
Characteristics of Human Rights :-
- Universality and Inalienability:
- Universality: Human rights are universal. Every person, regardless of nationality, place of residence, gender, national or ethnic origin, color, religion, language, or any other status, is entitled to these rights.
- Inalienability: Human rights cannot be taken away, except in specific situations and according to due process. For example, the right to liberty can be restricted if a person is found guilty of a crime by a court of law.
- Indivisibility:
- Human rights are indivisible. Whether they are civil and political rights, like the right to life, equality before the law, and freedom of expression, or economic, social, and cultural rights, such as the right to work, social security, and education, they are all inherent to the dignity of every human person. Consequently, they all have equal status as rights, and cannot be ranked in a hierarchy.
- Interdependence and Interrelatedness:
- The fulfillment of one right often depends, wholly or in part, upon the fulfillment of others. For example, the realization of the right to health may depend on the realization of the right to education or the right to information.
- Equality and Non-Discrimination:
- All individuals are equal as human beings and by virtue of the inherent dignity of each human person. All human beings are entitled to their human rights without discrimination of any kind, such as race, color, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth, or other status.
- Participation and Inclusion:
- Every person and all peoples are entitled to active, free, and meaningful participation in, contribution to, and enjoyment of civil, economic, social, cultural, and political development in which human rights and fundamental freedoms can be realized.
- Accountability and Rule of Law:
- States and other duty-bearers are answerable for the observance of human rights. In this regard, they have to comply with the legal norms and standards enshrined in human rights instruments. Where they fail to do so, aggrieved individuals or groups are entitled to adequate reparation, including, where appropriate, compensation.
Major Human Rights Documents and Declarations :-
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR): Adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1948, it sets out fundamental human rights to be universally protected.
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR): A key international treaty providing a range of protections for civil and political rights.
- International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR): Another crucial international treaty that ensures the protection of economic, social, and cultural rights.
Examples of Human Rights :-
- Right to life, liberty, and personal security
- Freedom from torture and degrading treatment
- Right to equality before the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Freedom of speech and expression
- Right to work and to receive fair wages
- Right to education
- Right to health and adequate medical care
Human rights are foundational principles that support the dignity and well-being of individuals and societies. Their protection and promotion are essential for achieving global peace, justice, and development.
